Google is explicitly identifying people it understands to be content creators.
This article explains how we know that Google is recognizing content creators, why it’s important and what SEO professionals need to do in response.
Google’s growing recognition of content creator entities
I recently discovered Knowledge Panel subtitles like “Content Creator (Medicine)” and “Content Creator (Travel)” in the SERPs.
This shows Google’s explicit identification of individuals as authoritative content creators within specific fields.
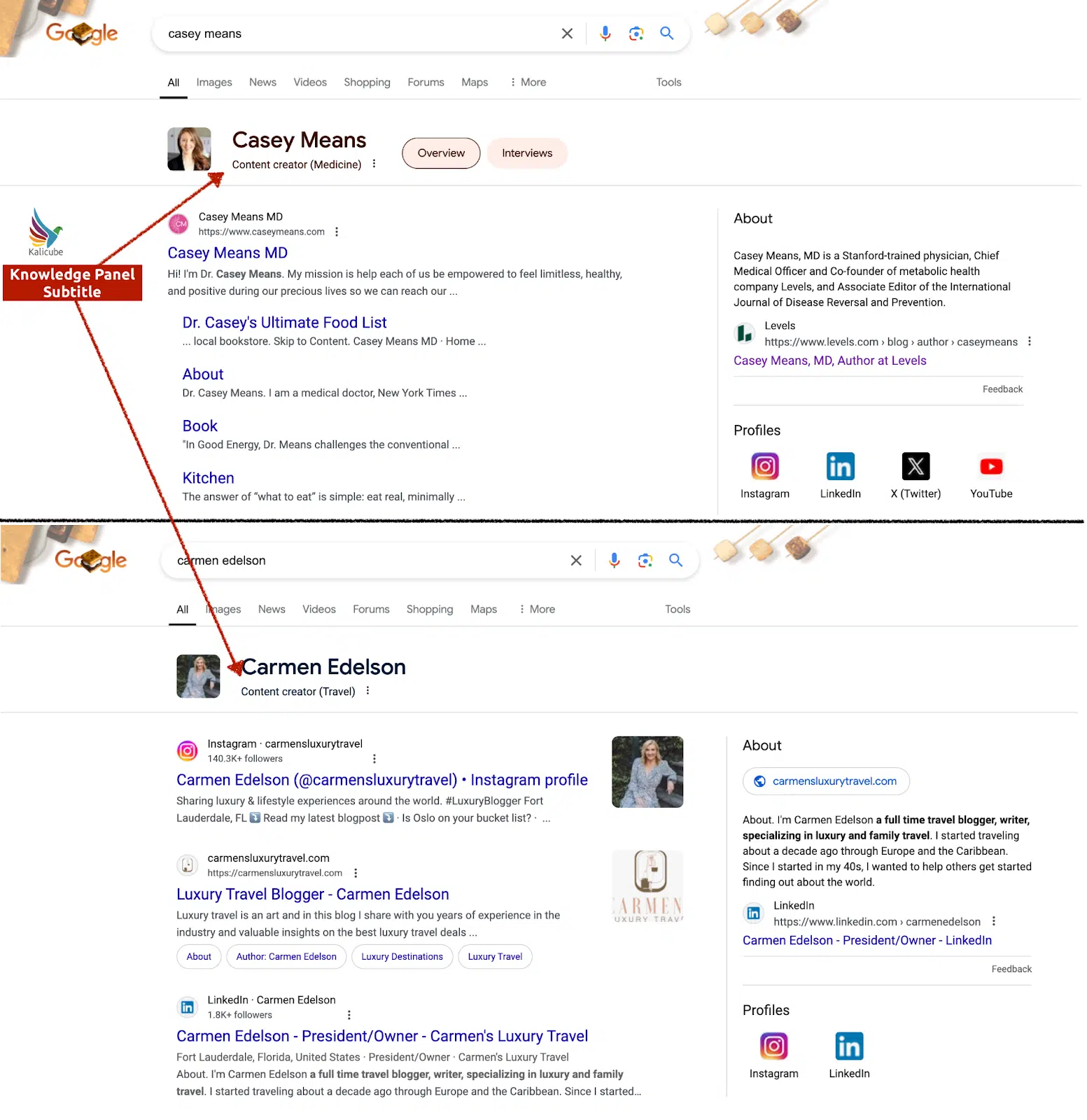
This is a significant E-E-A-T development for content creators as it gives visible and meaningful proof that Google has recognized them as credible sources of information on a specific topic.
It’s also a huge advantage in modern SEO, since the person’s content is more likely to appear in today’s search results and tomorrow’s AI-powered assistants.
Here are some examples from the Kalicube Pro dataset (tracking over 17 million person entities) for content creator topics:
- Agriculture, Animals, Art, Automobiles.
- Baking, Baseball, Beauty, Bodybuilding, Boxing.
- Camping, Cats, Coaching, Cooking, Cosmetics, Cricket, Cryptocurrency.
- Dancing, Dogs.
- Fashion, Fashion, Finances, Fishing, Food.
- Gambling, Games, Geography, Gymnastics.
- Health, Hiking, History, Humor.
- Interior design, Investing, Jazz, Law.
- Magic, Markets, Martial arts, Medicine, Mental health, Music.
- Nutrition, Painting, Parenting, Physical fitness, Politics, Psychology.
- Racing, Real Estate, Religion.
- Science, Shopping, Skincare, Soccer, Stand-up comedy, Surfing.
- Technology, Toys, Travel, Vegetarianism, Video games, Volleyball.
- Weather, Weight loss, Wildlife, Wrestling.
Google is looking for content creators
This focus on identifying content creators is a recurring theme at Google.
Three events in 2023 and 2024 demonstrated that identifying content creators is a major focus for Google:
- The Killer Whale Knowledge Graph update in July 2023.
- The March 2024 E-E-A-T update.
- The Google leak in May 2024 confirmed that Google explicitly associates people with their profile pages (isReference) and articles they have written (isAuthor).
Our Knowledge Graph monitoring tool shows small updates every 1 to 2 weeks. In 2024, they have mostly affected person entities.
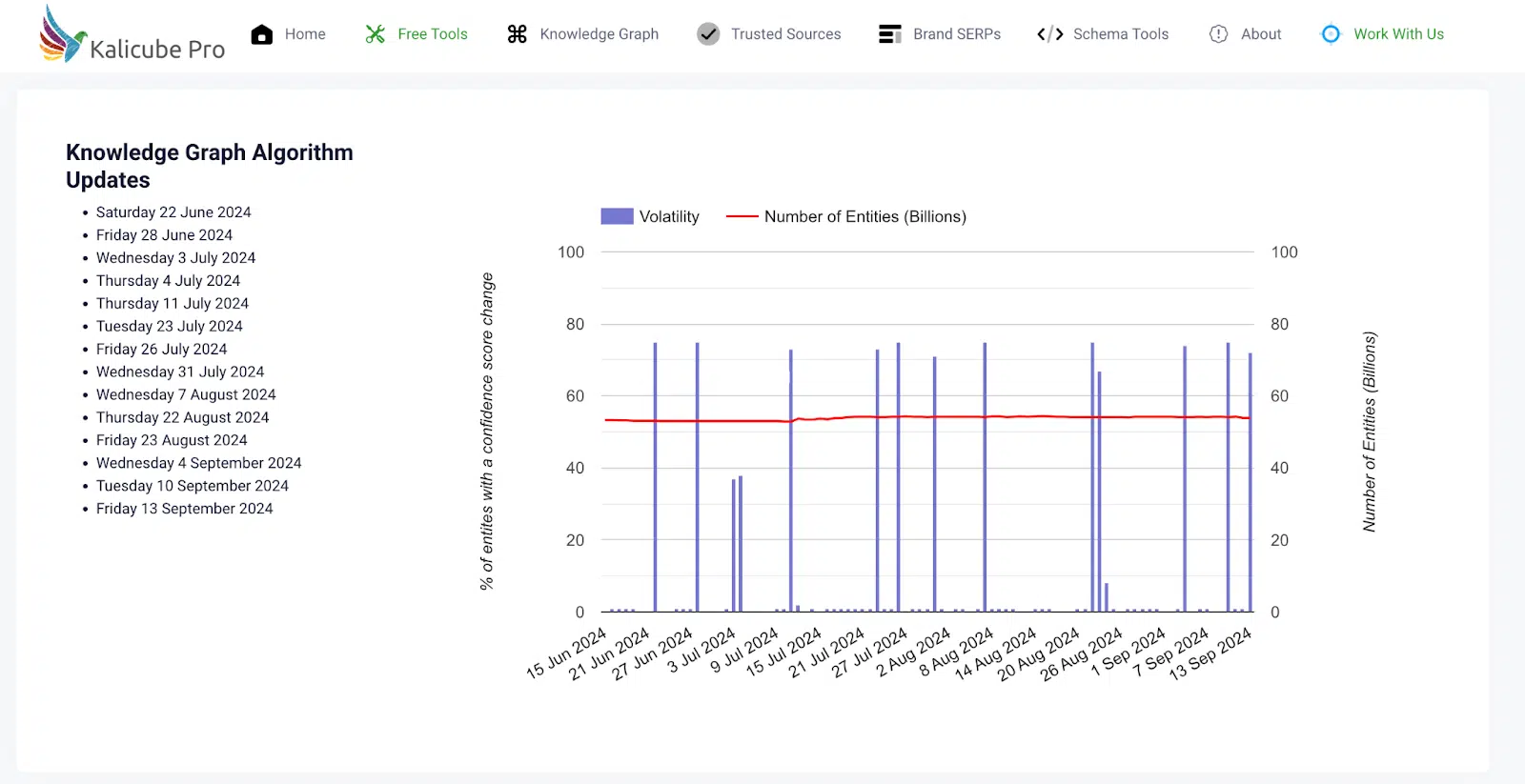
While these updates may seem random and impact around 10% of entities, they are typically minor “recalibrations” rather than strategically significant changes.
The key takeaway is that Google is increasingly focused on identifying trustworthy person entities and connecting them to the content they create.
Why this is important to E-E-A-T in SEO
E-E-A-T takes on real (measurable) meaning when Google identifies people it considers authoritative on a topic and can confidently link them to the content they create.
This places us firmly in the era of what I call modern SEO, where, in addition to optimizing the content (traditional SEO), optimizing the content creator and website publisher entities is necessary.
The logic is simple and irrefutable, given the data and the Google leak.
In order for Google’s algorithms to apply any E-E-A-T credibility signals, they need to understand the entity and the relationship between that entity and the web pages it creates or that provide information about it.
This is a zero-sum game. Without explicit understanding, the entity’s E-E-A-T credibility signals (links, awards, qualifications, reviews, testimonials, media coverage, etc.) will have no effect.
How to optimize content creator/author for SEO
To achieve optimal SEO results, you need to focus on optimizing both the content creator and website publisher entities. However, if you have to prioritize one, choose the content creator.
Google is increasingly focusing on individuals and optimizing content creators will likely provide the most value to your clients right now.
Optimization passes through three phases:
- Understandability.
- Credibility.
- Deliverability.
Understandability
Create clear relationships between the content creator and reference pages that Google can use to verify facts about the person. Ideal reference pages include:
- The creator’s personal website.
- The “About” page on their employer’s website.
- Social profiles.
- Trusted third-party sources like Crunchbase, Wikidata, etc.
Credibility
Establish connections between the content creator and relevant content. This includes:
- Articles they’ve written.
- Videos they’ve produced.
- Podcasts where they’ve appeared as a guest.
- Interviews they’ve participated in.
- Articles written about them.
Deliverability
Expand the content creator’s digital footprint by creating new content, getting content published about them and controlling all information strands. Ensure all content is:
- Clear.
- Consistent.
- Relevant.
- Topical.
- Factually accurate.
Use the creator’s personal website as a central hub in a hub-and-spoke model, linking all content to help Google and other AI systems connect the dots.
A simple, DIY method to check if Google recognizes the author
To see if Google recognizes an author, search for the title of one of their articles. In the SERPs, click the three vertical dots next to the result.
If Google shows the author’s name and a brief description, it means the relationship between the author and the content has been established in Google’s algorithms.
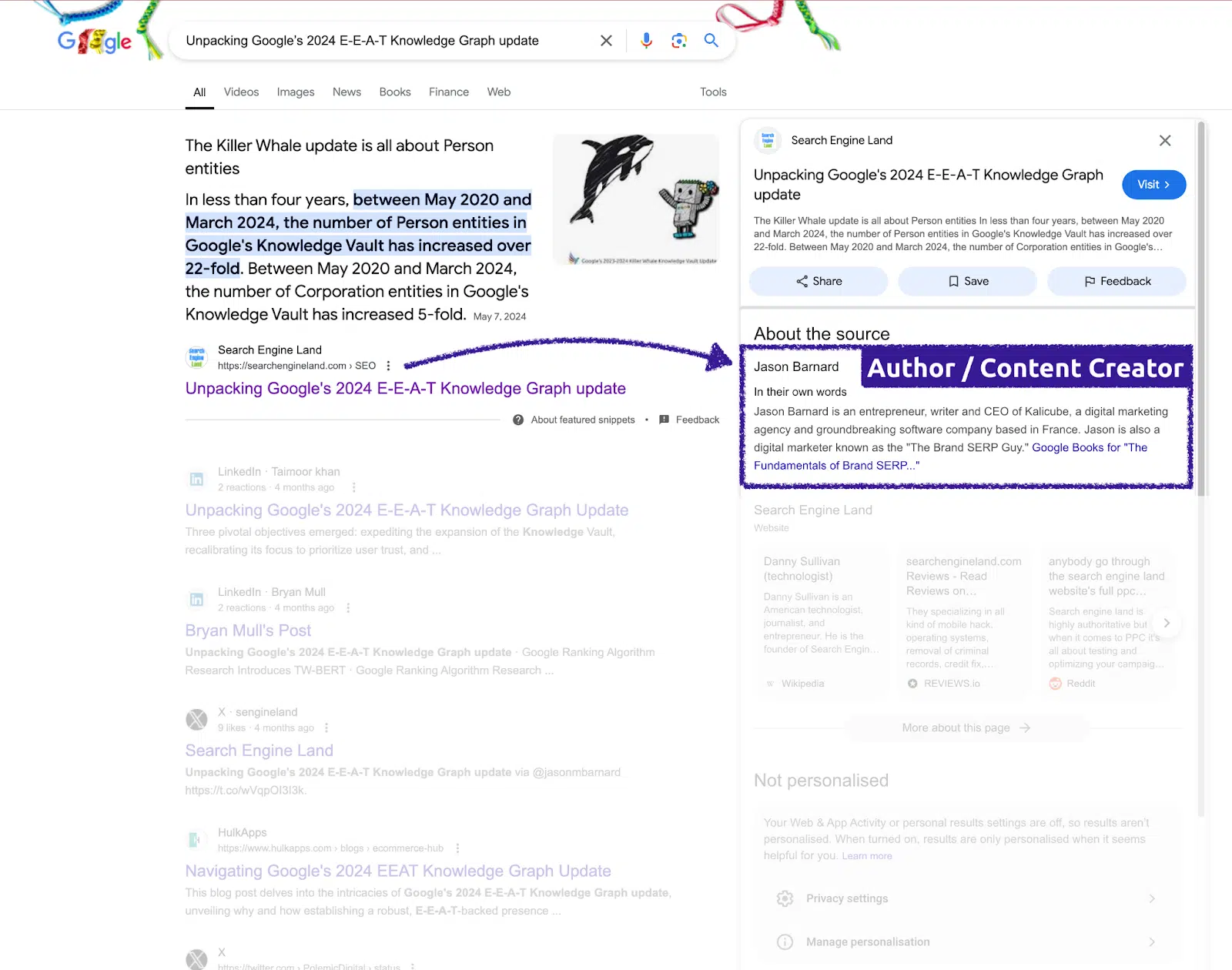
The person entity and URL relationships evolve over time
This strategy is not a “set-it-and-forget-it” approach. Over time, a person’s digital footprint expands, their niche evolves and Google’s dataset and algorithms continuously change.
For example, during the Killer Whale update, the number of person entities tripled in a single day, drastically altering the landscape for most entities overnight.
Even smaller updates can accumulate into significant changes:
- Seven minor updates In August and September led to the deletion of 19.21% of person entities and the creation of 21.26% new ones.
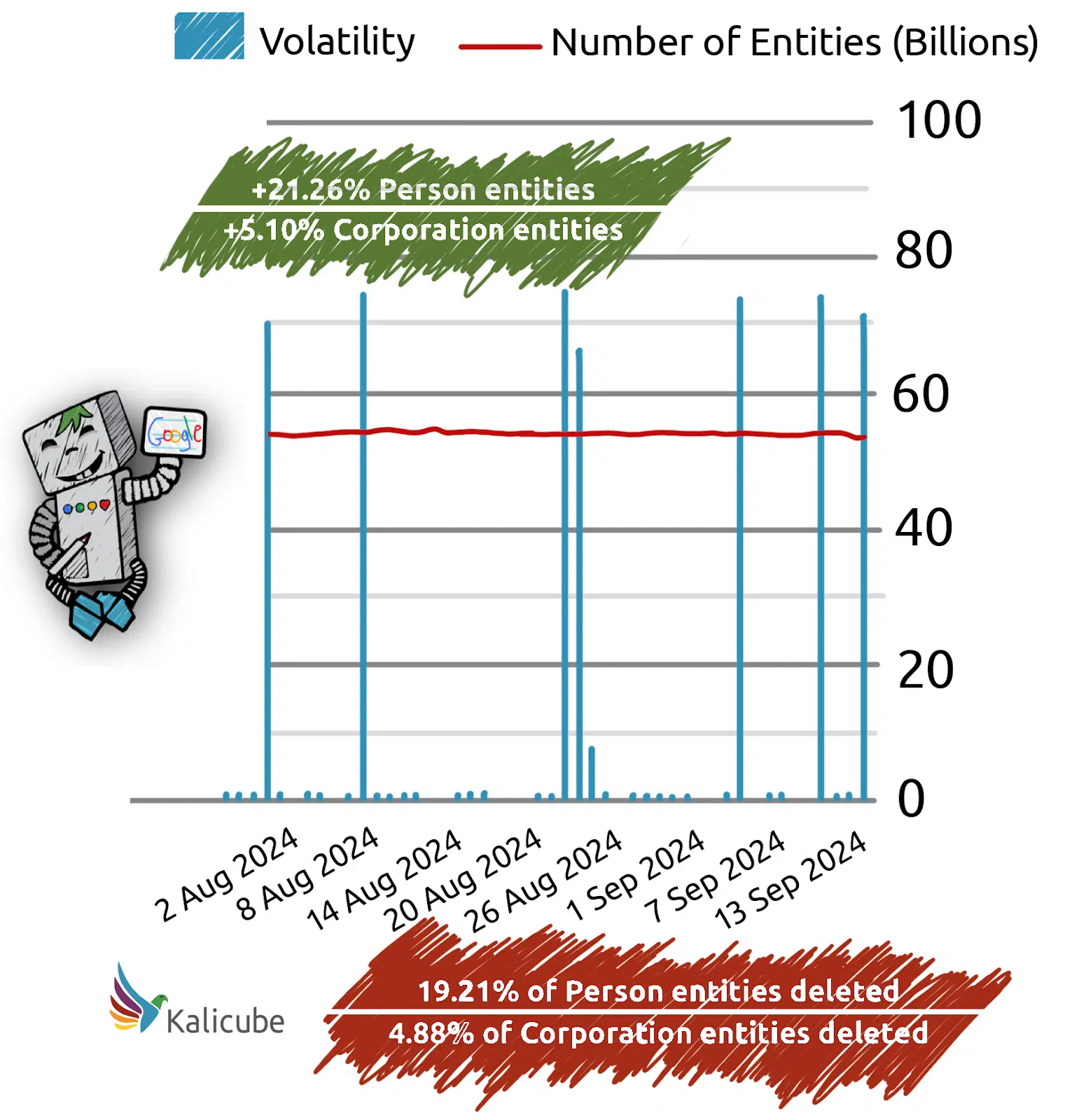
There is a constant risk of losing critical elements such as entity-to-reference relationships, author connections, specific facts about the entity and relationships with other entities.
The daily risk of losing their Knowledge Panel is particularly high for less established person entities.
Tracking these elements is essential, and ongoing maintenance is crucial.
We consider an entity to be established only after two years of presence in Google’s Knowledge Graph, as reflected in its entity home.
Entities that depend on sources like Wikipedia, Wikidata, Google Books, Crunchbase or other third-party resources for their existence in the Knowledge Graph remain vulnerable to changes in those sources.
Comments