SEO is a fast-moving, marketing-centric industry that will always keep you on your toes.
If you’re just getting started, it can be overwhelming without a guide.
There are many facets and specializations in SEO that come later in a career – local, technical, content, digital PR, UX, ecommerce, media – the list goes on.
However, that level of specialization isn’t something a junior professional needs to focus on right away.
Much like a liberal arts degree or an apprenticeship, a newcomer to SEO should first develop a broad understanding of the entire discipline before choosing a specialty.
This article covers several ways to build that foundational knowledge of search engine optimization.
1. Start with the business
Whether you’re in-house or at an agency, resist the urge to jump straight into “solution mode” when beginning an SEO project.
Instead of immediately focusing on meta tags, keywords, backlinks, or URL structure, start by understanding the business itself.
Here are some key questions to consider as you browse the website:
- What product or service is being sold?
- Who is the target audience? (If you’re in-house, who is your company trying to sell to?)
- Why does the company believe customers should choose them over competitors? (Common differentiators include price, unique features, or benefits.)
If you have the time or opportunity, dig deeper by asking your boss or client these business-focused questions:
- What are the company’s goals and targets?
- What is the three- to five-year plan for the business? (Are there plans to launch new products or expand into new markets?)
- Who are the main competitors, and what are they doing?

Even without that level of detail, the first three questions provide a useful frame of reference for determining the best SEO approach.
2. Be curious, ask questions
SEO now touches nearly every aspect of digital marketing.
Because of that, SEOs often become social butterflies, regularly collaborating with other departments and specialties.
I’ve been in SEO for 15 years now (which makes me feel old), but I continue to ask my clients questions every day.
This field encourages curiosity, so rather than feeling frustrated by what you don’t fully understand, embrace being the one to ask the “dumb questions.”
There’s no such thing as a dumb question, by the way.
Dig deeper: How to become exceptional at SEO
3. Build from the foundations of SEO
As mentioned earlier, SEO has many specializations. Some, like video or local SEO, are referred to as “search verticals.”
If you’re new to the field, start with the basics: the website and how Google presents search results.
Once you understand the business, try a simple exercise to analyze your site’s optimization.
Open a key product, category, or service page in one window. In another, search for a term you think users would enter to find that page.
Compare what appears in the search results with your own page and the pages that rank for that term.
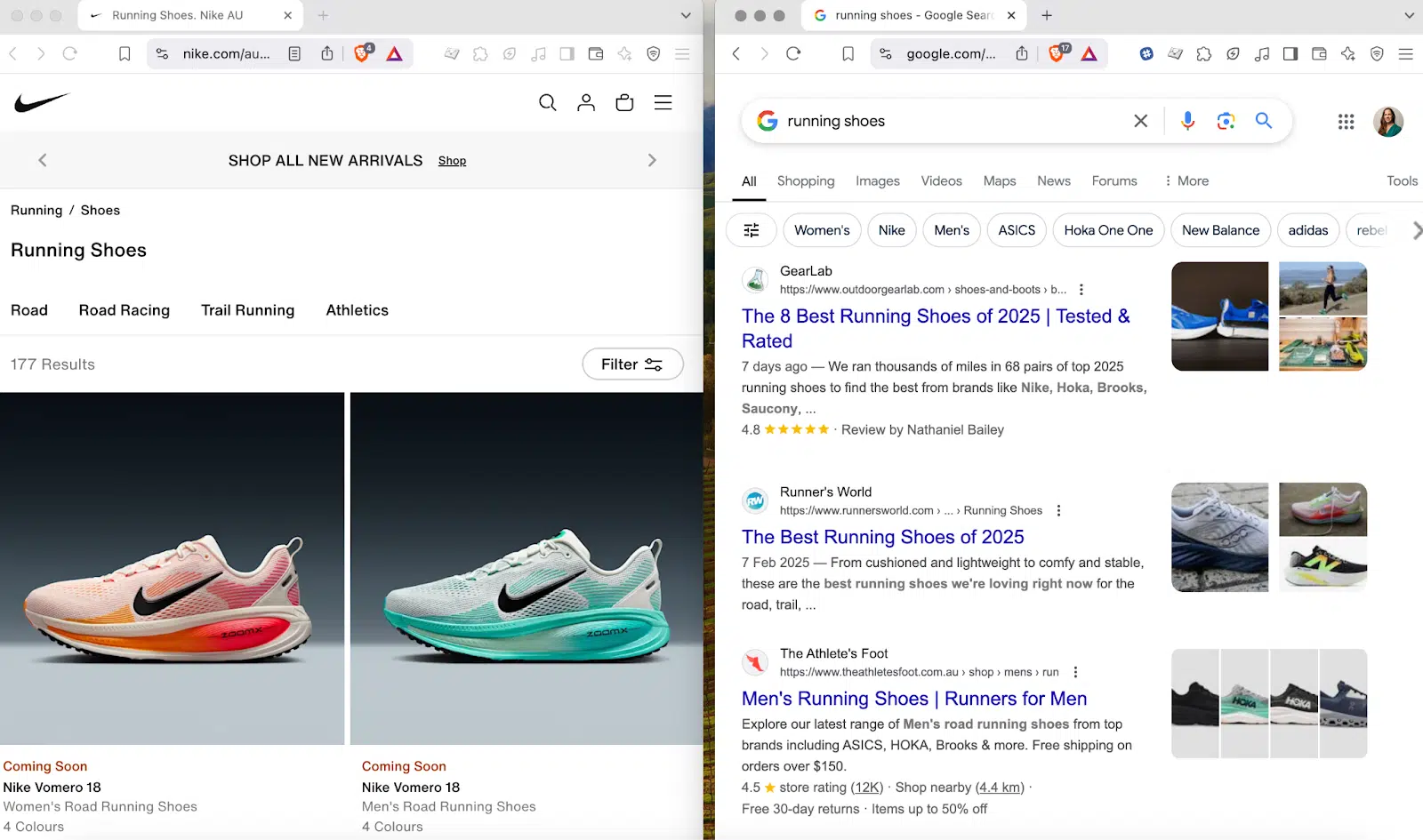
For example, in a search for “running shoes,” a few things stand out:
- The intent is somewhat mismatched. Nike’s category page targets users who are researching with intent to buy or are already planning a purchase. However, the search results display articles comparing different running shoes.
- Scrolling down, you might see an image carousel, a “Nearby Stores” section, and “People Also Ask” results.
If I were a new SEO at Nike and assumed the “running shoes” category page could rank for the “running shoes” query, I would rethink that after reviewing the search results.
If ranking for that broad term were a priority, I would create a running shoe comparison article featuring high-quality images of real people using the shoes – maybe even a video, if budget allowed.
If your page aligns more closely with the search results, analyze the top-ranking pages and adapt successful elements to your own site.
- Do most of them have an on-page FAQ while yours doesn’t?
- A product video? Detailed specs? User reviews?
Be critical and specific about what you can improve. (Never copy content directly.)
At its core, SEO is about identifying what Google deems important for a given product or service, then doing it better than the competition.
Many SEOs get caught up in tools and tactics and forget to examine the search results themselves.
Break that habit early and make reviewing Google’s search results a key part of your research process.
4. Dabble in the technical side and build relationships with your developers
Technical SEO is one of the more complex specializations in the field and can seem intimidating.
If you’re using a major CMS, your technical foundations are likely solid, so today, much of technical SEO focuses on refinements and enhancements.
While it’s important to develop technical knowledge, a great way to start is by building relationships with your development team and staying curious.
Asking questions makes learning more interactive and immediately relevant to your work.
Exploring coding courses or creating your own website can also help you develop technical skills gradually instead of all at once.
Some argue that you can be a good SEO without technical expertise – and I don’t disagree.
However, understanding a website’s inner workings, how Google operates, and even how large language models (LLMs) function can help you prioritize your SEO efforts.
Code is Google’s native language, and knowing how to interpret it can be invaluable when migrating a site, launching a new one, or diagnosing traffic drops.
Dig deeper: SEO prioritization: How to focus on what moves the needle
5. Learn the different types of information Google shows in search results
The way search results are presented today vastly differs from 10 or 15 years ago.
Those who have been in the industry for a while have had the advantage of adapting gradually as Google has evolved.
Newcomers, on the other hand, are thrown into the deep end, facing a wide range of search features all at once – some personalized, some not, and some appearing inconsistently.
This can be challenging to grasp, even for experienced SEOs.
Google has invested heavily in understanding user intent and presenting search results in a way that best addresses it.
As a result, search results may include:
- Videos.
- Images.
- People Also Ask.
- Related Searches.
- AI Overviews.
- AI-organized search.
- Map results.
- Nearby shopping options.
- Product listings.
- People Also Buy From.
- News
Building visibility for each of these features often requires a unique approach and specific considerations.
These search result types are now industry jargon, so a glossary can help you learn SEO terminology.
6. Learn the different types of query intent classifications
Google’s mission is to “organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.”
As part of this, Google works to understand why people search for something and provides the most relevant results to match that intent.
To do this, they classify queries based on intent.

The Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines, a handbook Google provides to evaluators who manually assess website and search result quality, also touches on understanding user intent:
“It can be helpful to think of queries as having one or more of the following intents.
- Know query, some of which are Know Simple queries.
- Do query, when the user is trying to accomplish a goal or engage in an activity.
- Website query, when the user is looking for a specific website or webpage.
- Visit-in-person query, some of which are looking for a specific business or organization, some of which are looking for a category of businesses.”
When conducting keyword research, it’s helpful to analyze both your site and the queries you’re targeting through this lens.
Many SEO professionals also use these broader, traditional intent categories, though they don’t always align perfectly with Google’s classifications:
- Informational: Who, what, when, where, how, why.
- Commercial: Comparison, review, best, specific product.
- Transactional: Buy, cheap, sale, register.
- Navigational: Searching for a specific brand.
Rather than focusing solely on keywords, take a step back and consider the intent behind the search. Understanding intent is essential for SEO success.
Dig deeper: Why traditional keyword research is failing and how to fix it with search intent
7. Do the research yourself before finding ways to use LLMs
Your company may already have guidelines for using LLMs like ChatGPT or Claude for tasks such as keyword research, content creation, or competitor analysis.
However, if you’re new to SEO, I strongly recommend completing at least one full project using tools like Google Search Console, Semrush, or Ahrefs without LLM support.
While AI can speed up the process, relying on it too early has drawbacks:
- Slower learning curve: If an LLM does the heavy lifting, you miss the experience of making strategic trade-offs, such as choosing a low-volume, mid-competition keyword over a high-volume, high-competition one.
- Lack of instinct for accuracy: Without firsthand research experience, it’s harder to recognize when an LLM generates inaccurate information or pulls from an unreliable source.
- Reduced impact: Google is increasingly sophisticated in detecting “repetitive content.” Relying too much on LLMs for mass content creation could hurt performance, whereas a more focused, strategic approach might yield better results.
While it may be tempting to jump straight into strategy rather than hands-on execution, senior SEOs develop their strategic mindset through years of practical work across different clients and industries.
Skipping this foundational experience could make it harder to recognize large-scale patterns and trends.
Dig deeper: Why you need humans, not just AI, to run great SEO campaigns
Laying the groundwork for SEO success
SEO offers endless opportunities once you master the fundamentals. If you’re just starting out, focus on these core areas:
- The business.
- The search results.
- User intent.
Keep it simple. Stay focused. Be business-led.
Build your SEO expertise on a strong foundation, and your career will grow from there.
Comments